A brand new learn about of Venus means that the deeply inhospitable global could also be extra like Earth than we concept.
A brand new delve into archival knowledge accumulated a long time in the past means that the alien planet has ongoing tectonic-like processes which can be deforming its floor and recycling its crust. If that is the case, then the massive, spherical options at the Venusian floor referred to as coronae could also be the important thing that unlocks our working out of the planet’s inside processes.
“Coronae are not found on Earth today; however, they may have existed when our planet was young and before plate tectonics had been established,” says planetary scientist Gael Cascioli of the University of Maryland and NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center.
“By combining gravity and topography data, this research has provided a new and important insight into the possible subsurface processes currently shaping the surface of Venus.”
Venus does not have tectonic plates, like Earth does. Here on our house global, the fragmented plates into which the crust is split generate a colourful, lively geology and floor options, permitting warmth to flee, and recycling crustal subject material.
Even with out tectonic plates, alternatively, the Venusian floor is riddled with proof of interior task that pushes up from under and creates deformations. One such function is the coronae. Coronae glance somewhat like have an effect on craters, consisting of a raised ring, like a crown, surrounding a sunken heart, with concentric fractures radiating outwards. They can also be masses of kilometers throughout.
Scientists first of all concept those buildings have been craters, however nearer research printed that they are volcanic in nature. They’re considered led to through plumes of scorching molten subject material welling up from the planet’s inside, pushing the outside upward right into a dome that then collapses inward when the plume cools. The molten subject material then leaks out of the perimeters of the collapsed dome to shape the hoop.
Although Venus does not have tectonic plates, tectonic task is assumed to exist within the type of interactions between mantle plumes and the lithosphere. The researchers concept that those interactions might be going on below the coronae.
frameborder=”0″ allow=”accelerometer; autoplay; clipboard-write; encrypted-media; gyroscope; picture-in-picture; web-share” referrerpolicy=”strict-origin-when-cross-origin” allowfullscreen>
They advanced fashions to explain other eventualities for the formation of coronae by means of plumes. Then, they when compared those fashions in opposition to gravity and topography observations accumulated through NASA’s Magellan probe, which spent a number of years orbiting and learning Venus within the 1990s.
They used the topography knowledge to spot 75 coronae, and the gravity knowledge to grasp what used to be happening beneath them. The workforce discovered that 52 of the coronae cap scorching, buoyant plumes of molten subject material which can be much less dense than the encompassing subject material, most likely riding tectonic processes.
There are two processes that happen right here on Earth which may be going down below coronae on Venus. The first is subduction. On Earth, that happens when the threshold of 1 tectonic plate will get slurped beneath the threshold of the adjoining plate.
On Venus, it might glance somewhat other. As a plume pushes upwards, it forces the outside subject material to unfold outwards and collide with different floor subject material, pushing some down into the mantle.
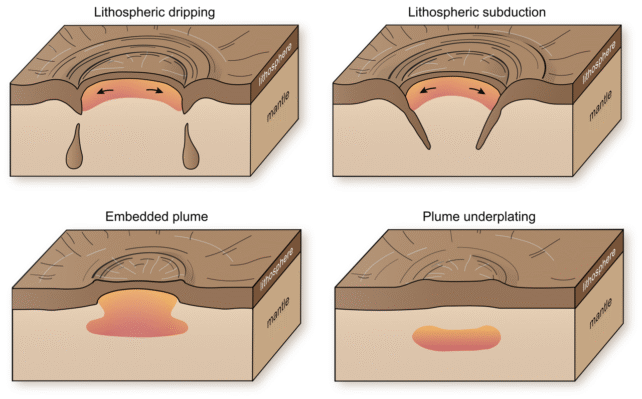
The different procedure is lithospheric dripping. As the bottom of the lithosphere, or crust, is heated from under, it could actually begin to soften itself, steadily forming oozy drips which can be nonetheless cooler and denser than the molten subject material under, so that they ultimately wreck off and cave in into the planetary inside.
We do not know needless to say, in fact. Between its searing floor temperatures, crushing atmospheric force, and acid rain, Venus items moderately a couple of obstacles to exploration. Nevertheless, coronae must, the scientists say, be a big center of attention for long term investigation, no longer least as a result of the possible parallels with our personal global.
“Coronae are abundant on Venus. They are very large features, and people have proposed different theories over the years as to how they formed,” says planetary scientist Anna Gülcher of the University of Bern in Switzerland.
“The most exciting thing for our study is that we can now say there are most likely various and ongoing active processes driving their formation. We believe these same processes may have occurred early in Earth’s history.”
The analysis has been revealed in Science Advances.
 Global News Post Fastest Global News Portal
Global News Post Fastest Global News Portal














