Your eyesight could be just right sufficient to with a bit of luck learn the tiny textual content on the optometrist from a couple of meters away. But you are left within the mud via a brand new instrument just lately demoed via researchers, which was once ready to scan tiny person characters of textual content from a distance of 1.36 kilometers (about 0.85 miles).
Intensity interferometry takes a unique option to imaging than standard cameras: somewhat than measuring gentle waves without delay, those gadgets measure the best way gentle displays and interferes with itself, then compiles a picture from that knowledge.
A brand new learn about, led via researchers from the University of Science and Technology of China, examined an device that emits 8 infrared laser beams fired throughout to a selected level within the distance.
Then, two telescopes have been used to seize the depth of the sunshine reflections. Through a cautious calibration of the 8 laser beams lights up the objective, the picture will also be reconstructed via evaluating diversifications between the readings from the 2 telescopes.
“Through outdoor experiments, we have successfully imaged millimeter-scale targets located at 1.36 km away, achieving a resolution enhancement by about 14 times over the diffraction limit of a single telescope,” write the researchers of their revealed paper.
Long vary cameras like this have makes use of in every single place from house telescopes to far off sensors, and the process used right here can care for atmospheric turbulence and higher organize imperfections within the digital camera setup.
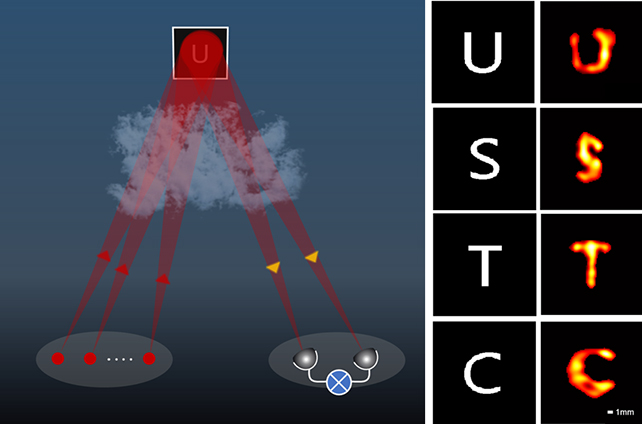
Through the setup described of their new learn about, the researchers have been ready to correctly learn letters at a solution of 3 mm. Using simply one of the most telescopes deployed right here by itself, on the similar distance, would’ve ended in a solution of 42 mm. That’s a large improve, and displays the opportunity of depth interferometry.
First utilized in house observatories, we are now seeing the tech being utilized in quite a few tactics on Earth, particularly in complex physics experiments. Previously, the means has been used to identify very shiny far away stars, or nearer items which might be lit up via a close-by supply – so it is a new building.
“The application of long-baseline active intensity interferometry holds promise for advancing high-resolution optical imaging and sensing,” write the researchers.
The approach that photons of sunshine bunch in combination and will also be interpreted via this tech is in fact a quantum impact that would not be predicted via commonplace physics, and that’s the reason one of the most a very powerful portions of the top solution right here.
Further enhancements are conceivable, the researchers say, in the best way the infrared laser lighting are managed. There’s additionally scope for including AI algorithms to the machine, to interpret explicit textual content and shapes extra correctly.
“The new work represents a significant technical advancement in imaging distant objects that do not emit their own light,” optics researcher Shaurya Aarav from Sorbonne University in France, who wasn’t concerned within the analysis, instructed Michael Schirber at Physics Magazine.
The analysis has been revealed in Physical Review Letters.
 Global News Post Fastest Global News Portal
Global News Post Fastest Global News Portal














