Scientists in China have evolved touch lenses that permit wearers see mild most often invisible to the human eye. Cooler nonetheless, the lenses paintings higher thru closed eyelids, and different variations may assist right kind shade blindness.
The human eye can see a rather restricted vary of colours – mild with wavelengths of between about 400 and 700 nanometers. In standard human-centric model, we name that the ‘visual’ a part of the spectrum, although different animals can see past it.
In a brand new find out about, scientists have helped people catch a glimpse of sunshine between 800 and 1,600 nanometers in period, a spread we most often cannot see referred to as infrared. The trick is to pop in a couple of touch lenses embedded with nanoparticles that convert the infrared wavelengths into visual ones.
The forte lenses do not disrupt a wearer’s skill to look visual mild, they simply upload infrared assets to the combo. In exams, wearers may establish flashing indicators from infrared LEDs and inform which course the sunshine was once coming from.
“It’s totally clear cut: without the contact lenses, the subject cannot see anything, but when they put them on, they can clearly see the flickering of the infrared light,” says Tian Xue, a neuroscientist on the University of Science and Technology of China.
Perhaps probably the most intriguing discovering is that wearers may nonetheless see the infrared mild with their eyes closed – in truth, their particular lenses gave the impression to paintings higher than having them open. That’s as a result of infrared mild penetrates deeper into the surface than visual mild, so the eyelids necessarily clear out the extra intense glare.
To be transparent, the wearers don’t seem to be seeing ‘new’ colours – that calls for a bulkier clinical setup. In this situation, the nanoparticles take in the infrared mild and convert it into acquainted, visual colours. It may assist us select up new details about the environment, with conceivable safety or encryption programs, the group says.
Going a step additional, the researchers confirmed {that a} extra detailed model of the touch lenses may let customers establish more than a few portions of the infrared spectrum. The nanoparticles color-coded infrared wavelengths, so mild at 808 nanometers seemed inexperienced, 980 nanometers was once blue, and 1,532 nanometers regarded purple.
Extending in this discovering, the group says it would sooner or later be tailored to assist color-blind other people see issues they most often cannot. Again, it would not disclose the lacking colours however convert the ones wavelengths into ones the individual’s eye can stumble on.
The problem of touch lenses is that they are so with regards to the retina that the transformed mild scatters, rendering issues a little blurry. Wearable glasses made with the similar nanoparticles allowed for higher-resolution infrared mild belief.
In follow-up exams with the ones glasses, the group was once even ready to turn how infrared mild reflecting off items may encode other knowledge that is invisible to the bare eye. Objects seem to us as sure colours on account of the particular patterns of visual mild that leap off them into our retinas. The similar factor occurs with infrared mild, however we simply (most often) cannot see it.
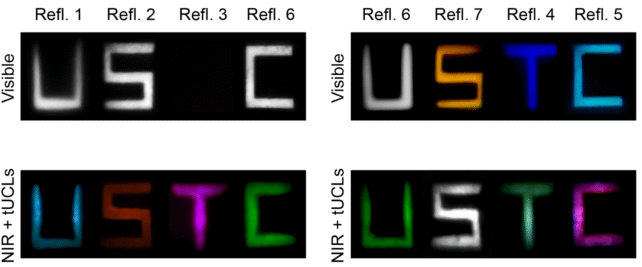
In exams, letters that seemed dull black or white to contributors no longer dressed in the glasses took on colourful colours once they put the fondness specifications on. That’s for the reason that infrared wavelengths bouncing off them had been transformed into explicit visual wavelengths by way of the glasses.
The thought of strolling round selecting up warmth signatures in the dead of night is a amusing one, however do not be expecting to be granted Predator-vision any time quickly. The nanoparticles can handiest select up infrared mild from robust LED assets for now, however the group hopes that the sensitivity may also be greater in long run paintings.
The analysis was once revealed within the magazine Cell.
 Global News Post Fastest Global News Portal
Global News Post Fastest Global News Portal














