US forecasters predict an above-normal 2025 Atlantic storm season, with 13 to 19 named storms, and 6 to 10 of the ones changing into hurricanes.
Every yr, the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration and different forecasters unlock preseason outlooks for the Atlantic’s storm season, which runs June 1 via Nov. 30.
So, how do they know what is more likely to occur months someday?
I’m an atmospheric scientist who research excessive climate. Let’s check out what Atlantic storm forecasts are in keeping with and why the ones forecasts can shift all the way through the season.
What is going right into a seasonal forecast
Think of the preseason storm forecast because the 30,000-foot view: It can not expect if or when a hurricane will hit a specific location, however it might probably be offering perception into what number of storms are more likely to shape all through all of the Atlantic, and the way energetic the season general could be.
These outlooks depend closely on two large-scale local weather elements.
The first is the sea floor temperature in spaces the place tropical cyclones have a tendency to shape and develop.
Hurricanes draw their power from heat ocean water. So when the Atlantic is surprisingly heat, as it’s been in recent times, it supplies extra gasoline for storms to shape and accentuate.
The 2d key component that meteorologists have their eye on is the El Niño–Southern Oscillation, which forecasters check with as ENSO. ENSO is a local weather cycle that shifts each and every few years between 3 major levels: El Niño, La Niña, and a impartial house that lives someplace in between.
During El Niño, winds over the Atlantic prime up within the troposphere – kind of 25,000 to 40,000 ft – toughen and will disrupt storms and hurricanes. La Niña, alternatively, has a tendency to scale back those winds, making it more straightforward for storms to shape and develop.
When you glance over the ancient storm list, La Niña years have tended to be busier than their El Niño opposite numbers, as we noticed from 2020 via 2023.
We’re within the impartial segment because the 2025 storm season starts, and most likely might be for no less than a couple of extra months. That method upper-level winds don’t seem to be specifically opposed to hurricanes, however they are no longer precisely rolling out the purple carpet both.
At the similar time, sea floor temperatures are working hotter than the 30-year reasonable, however no longer slightly on the record-breaking ranges observed in some fresh seasons.
Taken in combination, those prerequisites level to a slightly above-average storm season.
It’s vital to emphasise that those elements simply load the cube, tilting the chances towards extra or fewer storms, however no longer making certain an consequence. A bunch of alternative variables affect whether or not a hurricane in fact bureaucracy, how robust it turns into, and whether or not it ever threatens land.
The smaller influences forecasters can not see but
Once storm season is underway, forecasters get started paying shut consideration to shorter-term influences.
These subseasonal elements evolve briefly sufficient that they do not form all of the season. However, they may be able to noticeably elevate or decrease the probabilities for storms growing within the coming two to 4 weeks.
One issue is mud lofted from the Sahara Desert by way of robust winds and carried from east to west around the Atlantic.
These mud plumes have a tendency to suppress hurricanes by way of drying out the ambience and lowering daylight that reaches the sea floor. Dust outbreaks are next-to-impossible to expect months upfront, however satellite tv for pc observations of rising plumes may give forecasters a heads-up a pair weeks ahead of the mud reaches the main storm construction area off the coast of Africa.

Another key component that does not move into seasonal forecasts however turns into vital all the way through the season are African easterly waves. These “waves” are clusters of thunderstorms that roll off the West African coast, monitoring from east to west around the ocean.
Most primary storms within the Atlantic basin, particularly within the top months of August and September, can hint their origins again to the sort of waves.
Forecasters track robust waves as they start their westward adventure around the Atlantic, realizing they may be able to supply some perception about doable dangers to U.S. pursuits one to 2 weeks upfront.
Also on this subseasonal combine is the Madden–Julian Oscillation. The MJO is a wave-like pulse of atmospheric job that strikes slowly across the tropics each and every 30 to 60 days.
When the MJO is energetic over the Atlantic, it complements the formation of thunderstorms related to hurricanes. In its suppressed segment, hurricane job has a tendency to die down. The MJO does not ensure storms – or a loss of them – but it surely turns up or down the chances. Its segment and place may also be tracked two or 3 weeks upfront.
Lastly, forecasters will communicate in regards to the Loop Current, a deep river of heat water that flows from the Caribbean into the Gulf of Mexico.
When storms cross over the Loop Current or its heat eddies, they may be able to swiftly accentuate as a result of they’re drawing power from no longer simply the nice and cozy floor water however from heat water that is tens of meters deep. The Loop Current has helped energy a number of ancient Gulf storms, together with Hurricanes Katrina in 2005 and Ida in 2021.
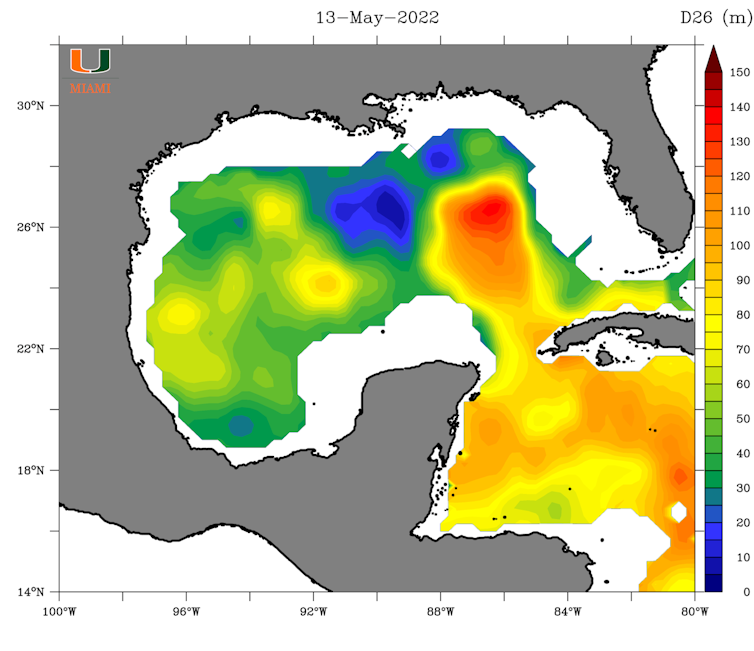
But the Loop Current is at all times moving. Its power and site in early summer time might glance very other by way of past due August or September.
Combined, those subseasonal alerts lend a hand forecasters fine-tune their outlooks because the season unfolds.
Where hurricanes shape shifts over the months
Where storms are maximum more likely to shape and make landfall additionally adjustments because the pages of the calendar flip.
In early summer time, the Gulf of Mexico warms up quicker than the open Atlantic, making it a notable hotspot for early-season tropical hurricane construction, particularly in June and July. The Texas coast, Louisiana, and the Florida Panhandle steadily face the next early-season possibility than places alongside the Eastern seaboard.
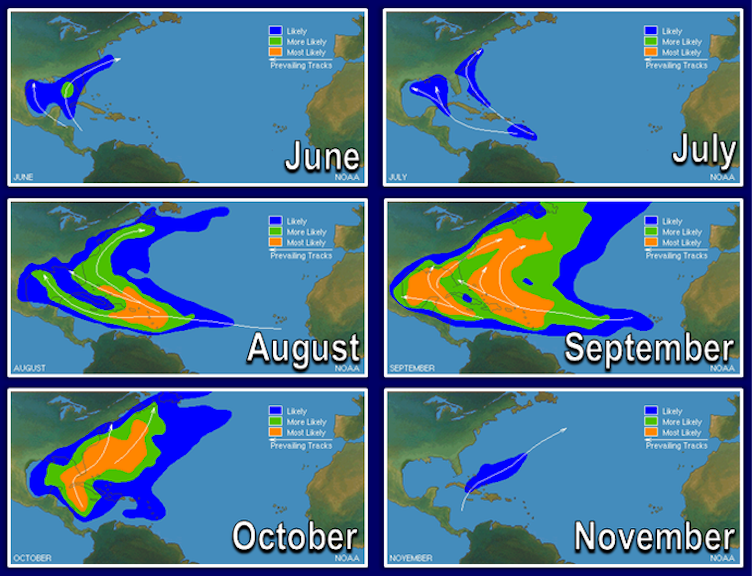
By August and September, the season reaches its top. This is when the ones waves shifting off the coast of Africa develop into a number one supply of hurricane job.
These long-track storms are often referred to as “Cape Verde hurricanes” as a result of they originate close to the Cape Verde Islands off the African coast. While many keep over open water, others can collect steam and tune towards the Caribbean, Florida or the Carolinas.
Later within the storm season, storms are much more likely to shape within the western Atlantic or Caribbean, the place waters are nonetheless heat and upper-level winds stay favorable. These late-season techniques have the next chance of following extraordinary paths, as Sandy did in 2012 when it struck the New York City area and Milton did in 2024 ahead of making landfall in Florida.
At the top of the day, the most secure method to consider storm season is that this: If you reside alongside the coast, do not let your guard down. Areas vulnerable to hurricanes are by no means completely immune from hurricanes, and it best takes one to make it a deadly – and unforgettable – season.![]()
Colin Zarzycki, Associate Professor of Meteorology and Climate Dynamics, Penn State
This article is republished from The Conversation beneath a Creative Commons license. Read the unique article.
 Global News Post Fastest Global News Portal
Global News Post Fastest Global News Portal














