The JWST has completed it once more. The tough house telescope has already printed the presence of shiny galaxies most effective a number of hundred million years after the Big Bang.
Now, it is sensed mild from a galaxy most effective 280 million years after the Big Bang, essentially the most far-off galaxy ever detected.
Prior to the JWST, we had no infrared telescopes with big enough mirrors to stumble on mild from the early galaxies.
The Hubble can see near-infrared mild, however most effective has a 2.4-meter replicate. It discovered just one galaxy from the Universe’s 500 million years. The Spitzer Space Telescope was once a devoted infrared telescope, however it most effective had an 85 cm replicate.
Not most effective does the JWST have a far higher replicate, however detector generation has complex such a lot that the veil obscuring the early Universe is being lifted one historic galaxy at a time.
One of the JWST’s number one science issues is the Assembly of Galaxies. We want to see the Universe’s earliest galaxies to know the way they shape and evolve. Within weeks of starting observations, the telescope discovered an abundance of shiny galaxies at redshifts more than z=10.
“This unexpected population has electrified the community and raised fundamental questions about galaxy formation in the first ≈ 500 Myrs,” the authors of a brand new paper write.
The JWST has constantly driven again our commentary horizon, and this latest detection displays it would possibly not have reached its prohibit but.
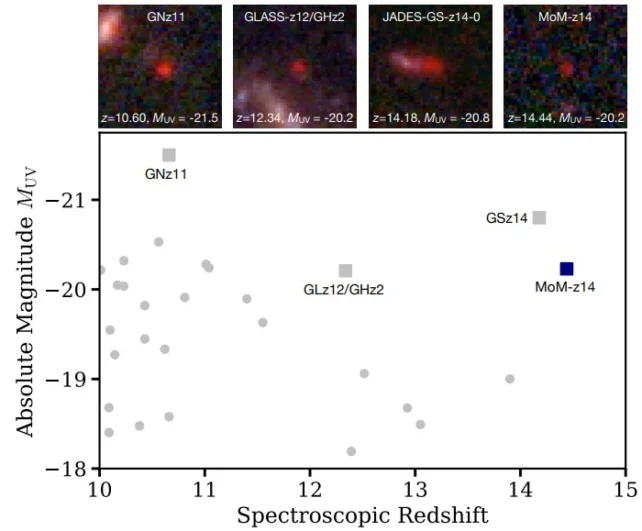
The newly found out galaxy is known as MoM-z14, and it comes from the Mirage or Miracle survey. This spectroscopic survey is designed to verify high-redshift candidate galaxies, and z14 refers back to the galaxy’s redshift. This discovering is unexpected as a result of astronomers anticipated to seek out only a few galaxies at any such excessive redshift.
The discovery is gifted in a brand new paper titled “A COSMIC MIRACLE: A REMARKABLY LUMINOUS GALAXY AT zspec = 14.44 CONFIRMED WITH JWST.” The lead creator is Rohan Naidu from the MIT Kavli Institute for Astrophysics and Space Research. The paper’s been submitted to the Open Journal of Astrophysics and is to be had at arXiv.org.
“JWST has revealed a stunning population of bright galaxies at surprisingly early epochs, z > 10, where few such sources were expected,” the authors write. At a redshift of z = 14.4, this galaxy “expands the observational frontier to a mere 280 million years after the Big Bang.”
They indicate that the JWST has discovered way more shiny galaxies between z = 14 and 15 than the consensus confirmed sooner than its release.
This find out about is not just any other interest. The spectroscopic exam printed attention-grabbing effects associated with the JWST’s Assembly of Galaxies theme.
Observations display that many of the galaxy’s mild comes from stars, no longer an energetic galactic nucleus (AGN). AGN are the brilliant cores of galaxies powered by way of supermassive black holes accreting subject. So MoM-z14 most likely hosts some luminous supermassive stars, one thing that principle predicted concerning the early Universe.
The galaxy’s nitrogen-to-carbon ratio is upper than that noticed within the Sun. Its chemical composition resembles historic globular clusters hooked up to the Milky Way. This implies that the celebrities within the galaxy and the ones in globular clusters shaped in identical environments with identical nucleosynthesis and metallicity air pollution from earlier stars.
“Since this abundance pattern is also common among the most ancient stars born in the Milky Way, we may be directly witnessing the formation of such stars in dense clusters, connecting galaxy evolution across the entire sweep of cosmic time,” the authors write.
There appear to be two morphologies for those historic shiny galaxies: level supply and prolonged. The relation between their morphologies and their chemistry is any other doable hyperlink in galaxy evolution.
“Furthermore, as noticed by Harikane et al. (2024b), these morphological differences are reflected in chemical abundance patterns, signalling a deeper connection between morphology and evolutionary pathways,” the authors write.
As the JWST has discovered extra historic shiny galaxies, a category of items which might be robust nitrogen emitters has change into obvious, together with luminous Little Red Dots. MoM-z14 might be a few of the maximum nitrogen-enhanced items the JWST has ever discovered.
“It adds further evidence for a size-chemistry bimodality at z > 10, wherein extended sources tend to be nitrogen weak while compact sources are strong N emitters,” the authors provide an explanation for.
The house science group waited a very long time for the JWST and its skill to watch the early Universe. While a few of its findings had been unexpected, this find out about displays how astronomers are discovering connections between the surprises printed within the early Universe and the fashionable Universe.
frameborder=”0″ allow=”accelerometer; autoplay; clipboard-write; encrypted-media; gyroscope; picture-in-picture; web-share” referrerpolicy=”strict-origin-when-cross-origin” allowfullscreen>
“We interpret MoM-z14 and N-emitters thru Galactic archaeology, connecting their abundance patterns to essentially the most historic stars born within the Milky Way at z ≳ 4 in addition to to globular clusters,” the authors write of their conclusion.
“The N-enhancement, brightness, hard ionizing spectra, stellar density, morphology, redshift dependence, and black hole fraction of these sources may be linked to globular cluster-like environments wherein runaway collisions may produce extraordinary objects such as supermassive stars.”
If it survives repeated cancellation threats, the Roman Space Telescope will have to disclose loads extra of these kinds of galaxies. A bigger dataset is all the time fascinating and would assist solidify a few of these findings, or perhaps introduce new mysteries. Either approach, it is going to be growth. But for now, the James Webb Space Telescope merits the highlight for this discovery.
“JWST itself appears poised to drive a series of great expansions of the cosmic frontier, previously unimaginable redshifts, approaching the era of the very first stars, no longer seem far away,” the researchers conclude.
This article was once at the start printed by way of Universe Today. Read the authentic article.
 Global News Post Fastest Global News Portal
Global News Post Fastest Global News Portal














