A brand new drug focused on irritation within the mind has been proven to strengthen the blood-brain barrier in mice, pioneering a possible shift within the struggle in opposition to neurodegenerative illnesses like Alzheimer’s.
“Finding [the drug] blocks brain inflammation and protects the blood-brain barrier was an exciting new discovery,” says pathologist Sanford Markowitz from Case Western Reserve University (CWRU).
What’s extra, the researchers word that amyloid ranges – the abnormally clumping proteins historically idea to play a job within the development of Alzheimer’s – remained the similar. This suggests the brand new remedy, that specialize in an immune protein known as 15-PGDH, goals an absolutely other physiological pathway than many present drugs.
“This is important because the most recently approved Alzheimer’s drugs focus only on removing amyloid and, unfortunately, don’t work very well and have risky side effects,” explains Markowitz. “Inhibiting 15-PGDH thus offers a completely new approach for Alzheimer’s disease treatment.”
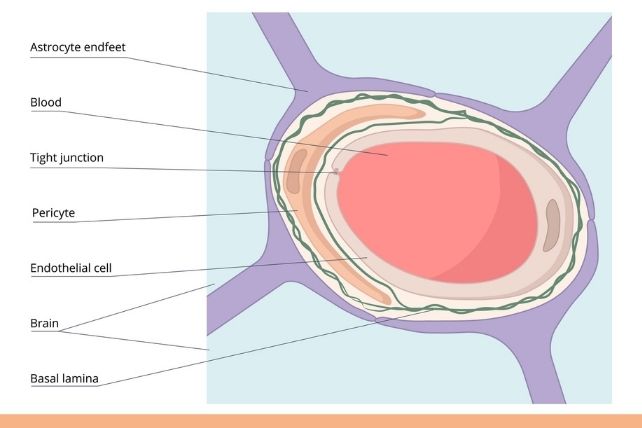
The blood-brain barrier is a layer of tissue that any substance coming into the mind by means of the blood will have to move via. When intact, the barrier filters out possible risks comparable to toxins, micro organism, and viruses.
Traumatic mind damage can harm this barrier, expanding dangers to mind cells. Such blood-brain barrier deterioration has additionally been recognized as a imaginable early indicator of dementias like Alzheimer’s.
By investigating the molecules lively throughout the blood-brain barrier cells, CWRU physiologist Yeojung Koh and co-workers have been ready to spot that the immune enzyme 15-PGDH was once increased in each mice and people with neurodegeneration bobbing up from age, damage, or illness.
In reaction, the researchers evolved SW033291; a compound that may block the enzyme’s job. The drugs was once discovered to effectively offer protection to the blood-brain barrier in mice and save you cognitive impairment even after demanding mind damage.
“In these mouse models treated with the drug, the blood-brain barrier remained completely undamaged,” says neuroscientist Andrew Pieper, additionally from CWRU. “The brains didn’t undergo neurodegeneration and, most importantly, cognition and memory capacity were completely preserved.”
With nearly 10 million new world instances of dementia annually, increasingly more folks face cognitive decline, both for my part or in family members. And in spite of many years of analysis, remedy results stay unclear. Exploring new ways like this is very important to making improvements to lives, however there may be nonetheless a protracted approach to cross.
“Our findings establish 15-PGDH as a guardian of blood-brain barrier integrity… and a compelling target for protection from neurodegenerative disease,” Koh and group write of their paper.
This analysis was once printed in PNAS.
 Global News Post Fastest Global News Portal
Global News Post Fastest Global News Portal














