A predator that swam Earth’s oceans greater than part a thousand million years in the past is not like any creature that lives on our planet these days.
Mosura fentoni possessed 3 eyes, grasped its prey with spiny claws, ate with a round, tooth-lined maw, swam with the help of flippers that coated each side of its frame, and had 26 frame segments – greater than every other radiodont, the extinct workforce of animals to which it belonged.
Luckily, it might most effective were about so long as your finger – maximum issues again then had been beautiful small. But its segmented tail finish has fascinated paleontologists Joe Moysiuk of the Manitoba Museum and Jean-Bernard Caron of the Royal Ontario Museum, who characterised the unusual beastie from its fossilized stays within the well-known Burgess Shale.
They named Mosura for its resemblance to a moth, despite the fact that the connection is far away and tenuous.
“Mosura has 16 tightly packed segments lined with gills at the rear end of its body,” Moysiuk explains. “This is a neat example of evolutionary convergence with modern groups, like horseshoe crabs, woodlice, and insects, which share a batch of segments bearing respiratory organs at the rear of the body.”
The oceans of Earth’s Cambrian duration, between round 539 and 487 million years in the past, had been a unique position than our planet these days. That used to be when lifestyles truly took off, and the sea began to thrive.
We do not have many information of that point, however the Burgess Shale is, truly, if we are being utterly frank, a wonder of fossil preservation. It shaped round 508 million years in the past, when silty dust flowed around the seafloor, trapping and protecting a lot of organisms because it went.
That dust was a fossil mattress referred to as a Lagerstätte, so remarkable that ins and outs, cushy tissue, or even inner constructions had been captured within the sediment. It printed a wealthy ecosystem stuffed with mysterious creatures so abnormal that we’ve got ceaselessly been left baffled and flawed about their anatomy.

In this surroundings lived the radiodonts, a bunch of animals that shared a not unusual ancestor with arthropods, however has since long gone extinct. This workforce contains the well-known Anomalocaris, a fearsome beast that may have grown as much as a meter lengthy. That may now not appear very huge to us, however again then, when maximum issues had been small, it used to be a large.
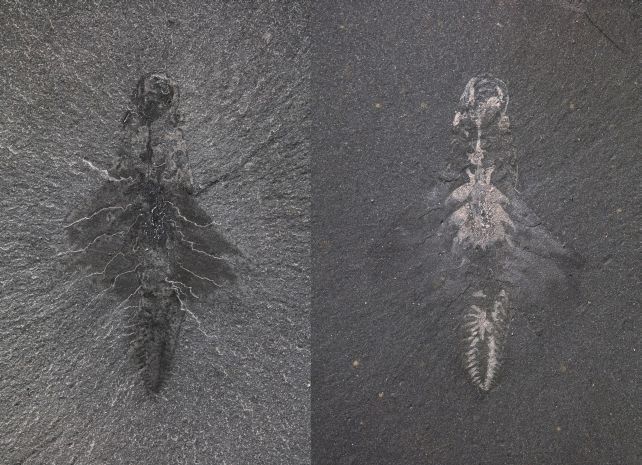
Mosura used to be now not a large, nevertheless it used to be one-of-a-kind, a minimum of so far as we all know. Moysiuk and Caron studied 61 fossilized people of the species, and characterised it intimately.
“Very few fossil sites in the world offer this level of insight into soft internal anatomy,” Caron says. “We can see traces representing bundles of nerves in the eyes that would have been involved in image processing, just like in living arthropods. The details are astounding.”
Of explicit pastime used to be the animal’s circulatory gadget. It didn’t contain veins, because the circulatory methods of vertebrates do, however used to be as a substitute open, just like the flow of recent arthropods. In crabs, spiders, bugs, and different arthropods, the center merely pumps blood (or hemolymph) into cavities of their our bodies, the place it swirls round their organs to accomplish its serve as.
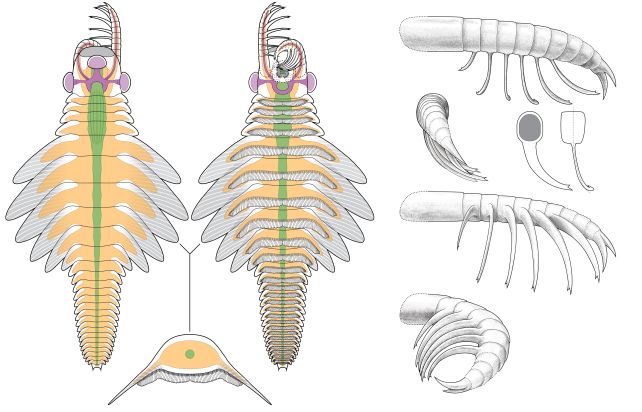
In Mosura, those cavities are referred to as lacunae. They stuffed the creature’s frame, and prolonged into the swimming flaps that prolonged from each and every section, visual as reflective patches within the fossils.
“The well-preserved lacunae of the circulatory system in Mosura help us to interpret similar, but less clear features that we’ve seen before in other fossils. Their identity has been controversial,” Moysiuk says. “It turns out that preservation of these structures is widespread, confirming the ancient origin of this type of circulatory system.”
As for its unusual, robust breathing gadget on the rear finish of its frame, its specialised construction suggests Mosura will have had distinctive wishes. Perhaps its habitat used to be other from that of alternative radiodonts, or possibly its looking strategies required enhanced breathing purposes.
This is a kind of questions this is unimaginable to respond to with out additional info. However, Mosura is a gorgeous instance of the methods lifestyles adopts to thrive in step with circumstance.
“Radiodonts were the first group of arthropods to branch out in the evolutionary tree, so they provide key insight into ancestral traits for the entire group,” Caron says. “The new species emphasizes that these early arthropods were already surprisingly diverse and were adapting in a comparable way to their distant modern relatives.”
The analysis has been printed in Royal Society Open Science.
 Global News Post Fastest Global News Portal
Global News Post Fastest Global News Portal














