A supermassive black hollow round 1,000,000 occasions the mass of the Sun simply gave away its place in impressive type.
When a passing superstar veered just a little too shut, it used to be torn aside within the black hollow’s gravitational subject, liberating a huge flare of sunshine.
That flare of sunshine, a tidal disruption match recorded by means of telescopes on Earth, used to be named AT2024tvd, and its detection printed one thing very abnormal concerning the galaxy 600 million light-years away by which the development came about.
The black hollow accountable, in line with a crew of astronomers led by means of Yuhan Yao of the University of California, Berkeley, is a wanderer, untethered from the nucleus of a galaxy. It isn’t even in a binary orbit with the supermassive black hollow that is on the center of the host galaxy.
“AT2024tvd is the first offset tidal disruption event (TDE) captured by optical sky surveys, and it opens up the entire possibility of uncovering this elusive population of wandering black holes with future sky surveys,” Yao says.
“Right now, theorists haven’t given much attention to offset TDEs. I think this discovery will motivate scientists to look for more examples of this type of event.”
Black holes, when they are simply lurking round in house, are very tough to identify, particularly in different galaxies. They do not emit any radiation we will be able to lately stumble on, and that’s the reason our primary instrument for finding out the cosmos. We can stumble on black hollow pairs by means of gravitational waves once they smack into each and every different, however a lone black hollow doing not anything is invisible.
There’s an exception. When one thing will get shut sufficient, the tough tidal forces throughout the black hollow’s gravity subject will rip it aside, and ship it spiraling down past the development horizon. This procedure, referred to as a tidal disruption, emits a blazing flare of sunshine around the electromagnetic spectrum that we will be able to stumble on from thousands and thousands to billions of light-years away, and deconstruct to be informed concerning the black hollow accountable.
AT2024tvd used to be simply this kind of flare, first detected on 25 August 2024 by means of the Zwicky Transient Facility, a wide-field sky survey designed to pick out up brief occasions like supernovae and TDEs. Astronomers hastily adopted up, the usage of radio, optical, and X-ray telescopes to seize as a lot of the development’s gentle as imaginable.
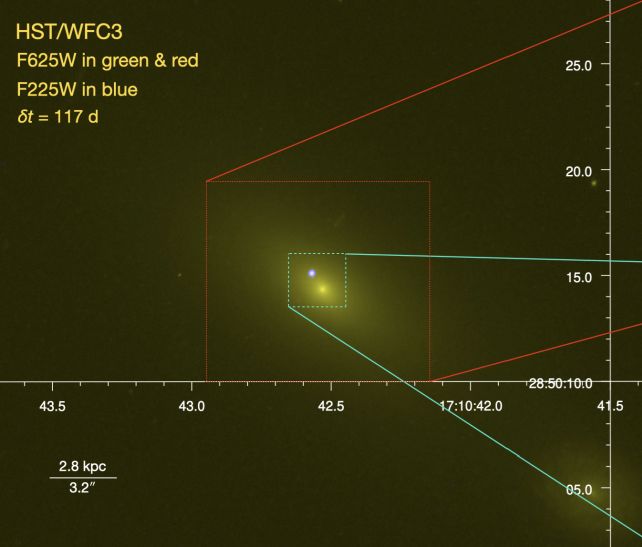
Yao and associates have been in a position to track the development to some extent within the sky 600 light-years away, the place, with ease, a big galaxy will also be discovered. But, even if their research printed a supermassive black hollow because the wrongdoer for the TDE with a mass between 100,000 and 10 million Suns, the purpose within the galaxy from which the flare originated used to be no longer the galactic middle.
This is in point of fact attention-grabbing. Supermassive black holes are most often discovered sitting within the facilities of galaxies – the gravitational hub round which all of the equipment and kaboodle revolves. AT2024tvd’s host galaxy, on the other hand, already has a supermassive black hollow in its middle, one that is round 100 million sun plenty.
Now, there are galactic facilities that experience two or extra supermassive black holes, locked in a gravitational dance that can sooner or later see them merge to shape one even huger black hollow.
However, the 2 supermassive black holes within the galaxy in query don’t seem to be gravitationally certain in a binary. They’re separated by means of a distance of round 2,600 light-years, and the smaller one is solely moseying concerning the galactic bulge.
frameborder=”0″ allow=”accelerometer; autoplay; clipboard-write; encrypted-media; gyroscope; picture-in-picture; web-share” referrerpolicy=”strict-origin-when-cross-origin” allowfullscreen>
Galaxies acquire additional supermassive black holes once they collide with different galaxies; over the years, the 2 supermassive black holes at their hearts to find each and every different, which is after we see them locked in combination as a gadget.
The presence of a 2nd supermassive black hollow on this specific galaxy implies that, sooner or later in its previous, it merged with every other galaxy.
What we do not know is whether or not it is on its manner into or out of the galactic middle. It’s fully imaginable that the middle already hosts a binary. If that is the case, then the 3rd black hollow could have as soon as been amongst them, and used to be booted out by means of a three-body interplay.
Or shall we simply have stuck it on an inbound trajectory on its technique to the middle, the place it is going to input a binary interplay with the black hollow already therein. Either state of affairs is imaginable.
One manner to be informed extra about this black hollow configuration is to seek out extra galaxies that experience in a similar way offset rogue supermassive black holes. This analysis, the crew says, gives a possible pathway to take action.
“Tidal disruption events hold great promise for illuminating the presence of massive black holes that we would otherwise not be able to detect,” says astronomer Ryan Chornock of UC Berkeley. “Theorists have predicted that a population of massive black holes located away from the centers of galaxies must exist, but now we can use TDEs to find them.”
The analysis has been approved into The Astrophysical Journal Letters, and is to be had on arXiv.
 Global News Post Fastest Global News Portal
Global News Post Fastest Global News Portal














